Get Involved with Recycling Lives Services for a Greener Future
Get Involved with Recycling Lives Services for a Greener Future
Blog Article
Discovering Different Sorts Of Waste in Modern Waste Management Systems
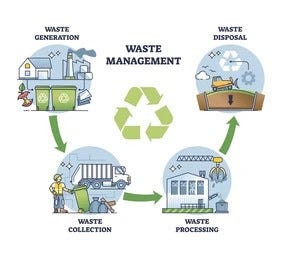
The contemporary landscape of waste management involves browsing a complicated variety of waste types, each requiring specialized handling and disposal methods to minimize ecological effects. Metropolitan strong waste, harmful waste, electronic waste, and natural waste each present distinct obstacles and chances for resource recuperation.
Local Solid Waste
Metropolitan solid waste, frequently described as family garbage or trash, encompasses a selection of discarded products produced by residential, industrial, and institutional sources within a district. This waste stream usually includes products such as packaging, food scraps, lawn trimmings, paper, plastics, textiles, and disposed of home items. The administration of municipal solid waste is a vital element of metropolitan preparation and public health, demanding reliable collection, transport, and disposal systems.
Effective waste management systems are developed to lessen ecological impact while taking full advantage of source recuperation. Composting natural waste, such as food scraps and backyard trimmings, not just reduces garbage dump usage however additionally produces valuable soil modifications.
Districts must likewise attend to the logistical and economic difficulties related to waste administration. Applying pay-as-you-throw systems, boosting public awareness, and investing in innovation can dramatically improve waste diversion rates. By integrating these methods, districts can foster sustainable areas, decrease greenhouse gas discharges, and preserve natural deposits.
Hazardous Waste
Efficient unsafe waste monitoring includes numerous essential actions: identification, disposal, segregation, and treatment. Partition makes sure that hazardous materials are saved independently from non-hazardous waste to stop cross-contamination.
Governing structures, such as the Source Preservation and Healing Act (RCRA) in the United States, give standards and criteria for contaminated materials monitoring. Adherence to these policies, coupled with improvements in waste therapy modern technologies, is crucial in mitigating the risks connected with contaminated materials.
Digital Waste
Electronic waste, typically referred to as e-waste, stands for a swiftly expanding challenge in waste monitoring systems internationally. This kind of waste includes thrown out digital tools and tools such as smart devices, computer systems, tvs, and other digital appliances. The rapid pace of technical improvement, coupled with lowering product life expectancies and consumer demand for the most recent gadgets, has actually significantly raised the volume of e-waste created each year.
E-waste is especially problematic because of its intricate composition, usually including unsafe substances like lead, cadmium, and mercury, which posture significant ecological and wellness dangers otherwise correctly handled. Alternatively, e-waste also consists of beneficial materials such as copper, gold, and silver, which can be recovered and recycled. The dual nature of e-waste-- both dangerous and beneficial-- requires customized handling, recycling, and disposal processes.
Efficient e-waste management involves strict regulative structures, durable collection systems, and progressed recycling innovations. Public understanding and engagement are crucial, as improper disposal methods, such as unlawful unloading and casual recycling, exacerbate environmental contamination and carcinogen. Boosting e-waste management techniques is crucial for alleviating environmental impact and recovering beneficial sources in a progressively digital world.

Organic Waste
Organic waste, consisting of kitchen area scraps, backyard trimmings, and agricultural deposits, represents a substantial portion of the international waste stream. This kind of waste is eco-friendly, implying it can be damaged down by bacteria right into simpler natural compounds. Regardless of its capacity for all-natural decomposition, incorrect monitoring of organic waste can cause negative environmental impacts, including the emission of greenhouse gases such as methane, which add to climate adjustment.
Reliable administration of organic waste is important for lessening these environmental effects (recycling lives services). Composting is a widely taken on method, transforming natural waste into nutrient-rich compost that can enhance soil wellness and agricultural efficiency. Additionally, anaerobic food digestion is an arising modern technology that converts organic waste right into biogas, a renewable energy source, and digestate, which can be made review use of as plant food
Municipalities and waste management entities need to apply robust organic waste collection and treatment programs to maximize the advantages of these procedures. Public education projects can also play a crucial function in encouraging families and companies to separate organic waste from other sorts of waste. By prioritizing the administration of organic waste, societies can decrease garbage dump use, lower greenhouse helpful hints gas discharges, and produce useful results for farming usage.

Innovative Waste Management
In the world of waste administration, ingenious approaches are transforming exactly how societies handle their refuse, aiming for sustainability and efficiency. One prominent technology is the implementation of smart waste bins geared up with sensors that monitor fill degrees and maximize collection courses.
One more remarkable growth is the adoption of waste-to-energy (WtE) innovations. By transforming non-recyclable waste into useful power through processes such as incineration and anaerobic digestion, WtE lowers garbage dump concern and supplies a renewable resource resource. Additionally, advancements in chemical reusing allow for the failure of complicated plastics into their initial monomers, enabling the development of new, high-quality plastic items.
Additionally, the circular economic climate model is getting traction, highlighting the layout of products and systems that focus on reusability and source effectiveness. This all natural approach motivates industries to minimize waste generation from the beginning. Via these innovative strategies, contemporary waste monitoring systems are not only attending to the prompt challenges of garbage read here disposal but additionally leading the way for a more sustainable future.
Final Thought
A thorough understanding of community solid waste, contaminated materials, electronic waste, and natural waste, coupled with the implementation of ingenious waste monitoring solutions, is critical for reducing environmental effects. Incorporating modern technologies such as clever waste containers and waste-to-energy systems can enhance effectiveness and sustainability. Efficient waste monitoring approaches not just foster source recovery however likewise promote public understanding and participation, ultimately adding to the advancement of a circular economic situation.
The modern landscape of waste management includes navigating a complex range of waste types, each requiring specialized handling and disposal methods to mitigate ecological influences. Metropolitan strong waste, harmful waste, digital waste, and organic waste each present distinct challenges and possibilities for source healing.Electronic waste, typically referred to as e-waste, represents a rapidly growing obstacle in waste monitoring systems globally. Via these cutting-edge techniques, modern waste monitoring systems are not just resolving the instant challenges of waste disposal yet likewise paving the means for a much more sustainable future.
A comprehensive understanding of metropolitan solid waste, hazardous waste, digital waste, and organic waste, coupled with the execution of innovative waste monitoring options, is necessary for alleviating environmental influences. (recycling lives services)
Report this page